Fundamentals of Robotics provides students with a unique opportunity to gain experience and skill in robotic operation and programming through an industrial robotic training simulation software. This module features RoboCell, a 3D-solid modeling robotic simulation software, which allows students to expand their programming skills through a variety of simulated robotic workcells.
This module gives students the fundamental skills needed to operate, maintain, program and test robotic systems. The activities challenge students to design solutions for industrial robotic applications, with emphasis on real industrial concerns, such as recording accurate positions, optimizing programming and increasing productivity.
Catalog number: 88-3046-0000
[Ver: 2.1.2.1]
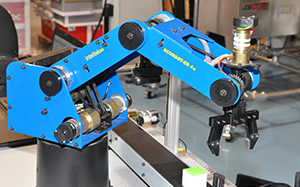
For students who have completed the Fundamentals of Robotics module, the Advanced Robotic Programming module offers the opportunity to further explore robotic programming. Using RoboCell, the same 3D-solid modeling robotic simulation software that the student has previously used, Advanced Robotic Programming gives the students a greater understanding of the robotics concepts and programming commands they have already learned, as well as the ability to extend that knowledge to gain a greater understanding of robot capabilities, of working with and manipulating a robot, and accomplishing various tasks while focusing both on the goal as well as programming skills and program efficiency.
This module gives students the advanced skills needed to operate, maintain, program and test robotic systems. The activities challenge students to design solutions for industrial robotic applications, with an emphasis on real industrial concerns, such as recording accurate positions, optimizing programming and increasing productivity.
Catalog Number 88-3048-0000
[Ver: 2.0.2.0]
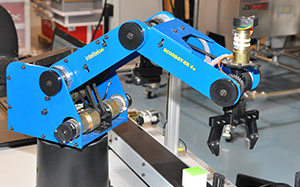
Robotics and Materials Handling gives students the fundamental skills needed to operate, maintain, program and test robotic systems. The lab version enables students to gain experience and skill in robotic operation and programming using the SCORBOT-ER4u, an industrial training robot. Using SCORBASE software, an intuitive tool for robot programming and control, students develop and write robot programs and design solutions for industrial robotic applications.
Cat. Number 77-8082-0000
[Ver: 2.0.0.0]
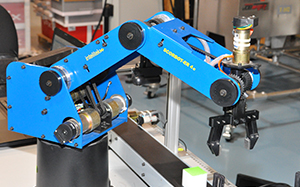
For students who have completed the Robotics and Materials Handling 1 module, the Robotics and Materials 2 module offers the opportunity to further explore robotic programming. Using RoboCell, a 3D-solid modeling robotic simulation software that uses SCORBASE, the same programming language that the student previously used, this module gives the students a greater understanding of the robotics concepts and programming commands they have already learned.
This module is a unique complement to the Robotics and Materials Handling 1 module in that it offers students who previously worked online with an industrial training robot to explore robotic simulations. Students are able to learn the advantages of simulating a project before working with a robot. Using the simulation software, students are also able to extend their existing knowledge or robotic programming to gain a greater understanding of robot capabilities, of working with and manipulating a robot, and accomplishing various tasks while focusing both on the goal as well as programming skills and program efficiency.
This module gives students the advanced skills needed to operate, maintain, program and test robotic systems. The activities challenge students to design solutions for industrial robotic applications, with an emphasis on real industrial concerns, such as recording accurate positions, optimizing programming and increasing productivity.
Cat. Number 88-8083-0000
[Ver: 2.0.1.0]

In the Automated Welding module, students discover robotic welding fundamentals by first working through the entire welding process in simulation. Only then can they execute actual automated welding applications.
Activities challenge students to develop solutions for common welding problems, such as thermal deformation, by adjusting their welding technique. Students also learn to improve weld quality by optimizing important welding parameters such as wire feed rate, robot speed, inert gas shield and voltage.
Catalog Number: 77-3001-0000
[Ver: 2.0.0.0]
